Crypto Asset Applications in Business
The crypto asset sector, and in particular cryptocurrencies, has experienced exponential growth in recent years. In this blog, we'll explore various cryptocurrency applications and their potential applications in businesses.
In recent years, the cryptocurrency sector has experienced significant growth, with a large number and variety of cryptocurrencies emerging (as of May 12, there were over 19,000) and a substantial increase in their overall market capitalization (approximately $1,160 billion on the same date).
Bitcoin is the leading protocol in the cryptocurrency industry, with a market dominance of approximately 40-45% over the past year. The second most capitalized cryptocurrency is the Ethereum protocol, which has a market dominance of around 18-20% during the same period.
As the cryptocurrency sector has grown, it has attracted increased interest from institutional and corporate players who weren't significantly involved in the "first wave" of cryptocurrency adoption, at least not in Italy or Europe. In contrast, the situation in the United States is noticeably different, where companies like Microstrategy and Tesla, have purchased and 'hodled' Bitcoins
in their treasury and are looking to hold the asset as part of a long-term strategic investment. Similarly, NASDAQ-listed exchanges like Coinbase have emerged in the US.
The use of crypto assets for businesses and traditional finance (TradFi) has significantly increased, leading to the emergence of a growing ecosystem of start-ups and entities that specialize in providing crypto services to these industries.
There are many different use cases for companies in the cryptocurrency sector. For example, NFTs have become a popular area, experiencing a significant boom despite only having about a year of history. This has led many companies, particularly those in the fashion, food, and luxury sectors, to launch NFT projects that have varying degrees of connection to physical assets, various intentions and or 'utilities'.
One of the earliest use cases for cryptocurrencies in the corporate context involves using them as assets for investment purposes. For example, MicroStrategy, a company listed on the NASDAQ Global Select Market, has adopted a new capital reserve policy where their assets include cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments, and bitcoins. The company's CEO, Michael Saylor, is a prominent advocate of Bitcoin globally and has been leading the way for the company's Bitcoin investments. In 2021, MicroStrategy adopted a corporate strategy of acquiring and holding bitcoin, while occasionally issuing debt or equity securities for capital raising transactions to purchase more bitcoin. The company views its bitcoin holdings as long-term and does not plan to trade them regularly. However, the company's financial statements clearly outline the various risks of their investment strategy, which provides valuable insights for other companies looking to follow in their footsteps. As of May 2022, MicroStrategy has invested approximately $3.965 billion in bitcoins, with an average unit purchase price of around $30,700 per bitcoin. Nevertheless, the financial statements also clearly outline the various risks of the strategy adopted by the company, and this listing provides an extremely useful overview for companies wishing to replicate this approach:
The price of Bitcoin can be influenced by unpredictable regulatory, commercial, and technical factors. Any changes in the Bitcoin price are likely to impact a company's financial results and share price;
The financial statements from previous years may not accurately reflect the potential changes in earnings that the company may face in the future due to its investment in bitcoin;
The company's financial statements from previous years do not reflect the potential variability of earnings that may arise from the company's investment in bitcoin. Additionally, changes in securities and financial market regulation may negatively impact the market price of the company's ordinary class A shares. This is because if investors view the company's shares as linked to the value of bitcoins held by the company, the introduction of bitcoin ETFs on US national securities exchanges could significantly reduce the market price of the company's shares;
The investment in bitcoin may be subject to SEC scrutiny as a NASDAQ-listed company;
The unregulated nature and lack of transparency surrounding the operations of many bitcoin exchange venues, they may experience fraud, security issues or operational problems, which may negatively impact the value of bitcoin;
The concentration of bitcoin holdings increases the risks inherent in the bitcoin acquisition strategy, as the lack of diversification increases the risks inherent in the bitcoin acquisition strategy; and
The bitcoin holdings are less liquid than cash and cash equivalents, and may not be able to serve as a source of liquidity to the same extent as cash and cash equivalents;
if the company or its third party service providers suffer a security breach or cyber attack and unauthorized parties gain access to the company's bitcoins, the company may lose some or all of its bitcoins and its financial condition and results of operations may be materially adversely affected
the loss or destruction of a private key required to access bitcoins may be irreversible. If the Company is unable to access its private keys or suffers a cyber attack or other data loss related to its bitcoins, our financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected
a regulatory change that reclassifies bitcoin as a "security" or financial instrument could result in the company being classified as an "investment company" under the Investment Company Act of 1940, and could adversely affect the market price of the bitcoin and the market price of the shares;
a significant decline in the market value of the bitcoins held could adversely affect the company's ability to incur debt.
CRYPTO ASSET APPLICATIONS IN BUSINESS:
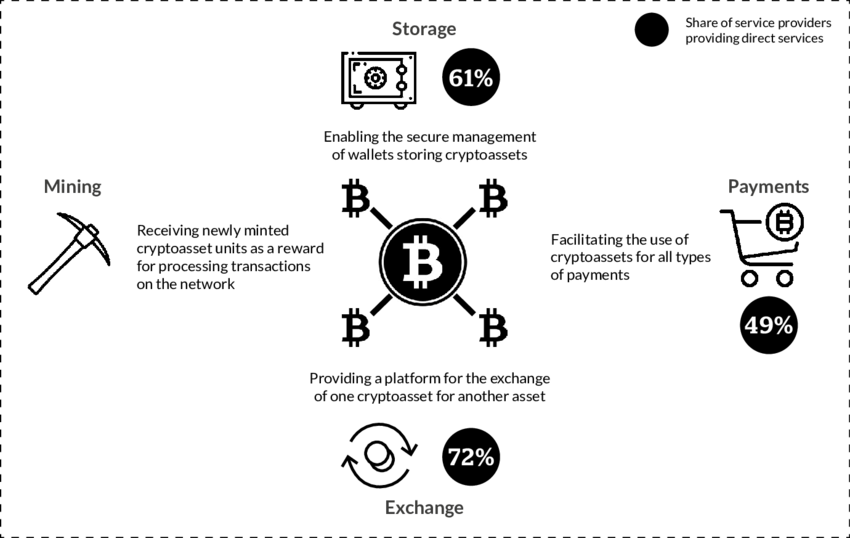
Payment processing: Cryptocurrencies can be used as a means of payment for goods and services. They offer fast, secure, and low-cost transactions compared to traditional payment methods.
International transactions: Cryptocurrencies can be used for cross-border transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks or other financial institutions. This can reduce transaction costs and increase the speed of transactions.
Investments: Some businesses use cryptocurrencies as a means of investment, either by buying and holding them as a long-term investment or by trading them for short-term profits.
Crowdfunding: Cryptocurrencies can be used for crowdfunding, enabling businesses to raise funds from a larger pool of investors, regardless of their location.
Decentralized applications: Cryptocurrencies can be used to develop decentralized applications (DApps) that operate on blockchain technology. These DApps can facilitate various business processes such as supply chain management, identity verification, and smart contracts.
Loyalty programs: Cryptocurrencies can be used to incentivize customers and create loyalty programs. Businesses can offer rewards in the form of cryptocurrency to customers for specific actions such as purchasing products, referring new customers, or participating in surveys.
Overall, cryptocurrencies offer many potential benefits for businesses, including increased efficiency, cost savings, and new opportunities for innovation. However, there are also risks and challenges associated with the use of cryptocurrencies, such as regulatory uncertainty and market volatility, that businesses need to consider before adopting them.